 |
These are many of the common words that have definitions in the springmaking field. The definitions are my own (caveat) and are admittedly not complete. This is not a dictionary -- it's just another tool you can use to do a better job.
 |
| Active coil | A coil of wire which contributes to the motive force of a spring. In extension and torsion springs, all the coils are active coils. In compression springs, only the coils which show daylight between them are active coils. |
| Arbor | A bar or pipe around which wire is wound to form a spring. |
| Back gear | A mechanism in a lathe that allows the chuck to turn very slowly. |
| Beryllium copper (wire) | An exotic material that can be made into springs. |
| Bundle | A roll or coil of wire as it is shipped from the manufacturer. |
| Cast | The curvature in wire that results from its being bundled into coils at the factory. |
| Chrome Silicon (wire) | An alloy of steel, stronger than Oil Tempered wire. |
| Chrome Vanadium (wire) | An alloy of steel, stronger than Oil Tempered wire. |
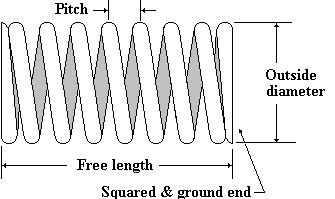
| Closed and ground end | Referring to the end of a compression spring where the wire forms one dead coil and is ground square. |
| Closed end | Referring to the end of a compression spring where the wire forms one dead coil and is not ground square. |
| Coil | 1) (noun) The wire of a spring going completely around once (see active coil, dead coil). |
| 2) (noun) A bundle of wire as it is shipped from the factory. | |
| 3) (verb) To form (wire) into a spring. | |
| Compression | Making smaller. |
| Compression spring | A spring which derives its usefulness because it pushes against a load which makes it smaller. |
| Dead coil | A coil of wire which does not contribute to the motive force of a spring. In extension and torsion springs, there are no dead coils. In compression springs, the coils at each end that lay against each other are dead coils: all the rest are active coils. |
| Double torsion | A form of torsion spring that has two coils; one left-handed and one right-handed, connected by a central tongue. |
| Extension | Making longer. |
| Extension spring | A spring which derives its usefulness because it pulls against a load which makes it longer. |
| Free length | The length of a spring with no load applied. |
| Grinding stage | A flat (usually) steel platform used to ensure that the ends of compression springs orient correctly to a grinding wheel. |
| Heat treat(ing) | 1) The process of tempering metal. |
| 2) (colloquially) The process of stress relief. | |
| Lathe | A machine which derives its usefulness by rotating stock against which tooling may be brought to bear. Springs are often wound on a lathe. |
| Lead screw | A mechanism in a lathe that allows the tool post to move from side to side at a precise rate. |
| Mandrel | An arbor. |
| Music wire | A high-carbon steel alloy used in making springs. |
| Open end | Referring to the end of a compression spring where the pitch of the spring extends all the way to the end of the wire, and does not form any dead coils. |
| OT (Oil Tempered wire) | A lower-carbon steel alloy used in making springs. |
| Passivate (-ation) | The process of removing chemical coatings from stainless steel by immersion in an acid bath. |
| Phosphor bronze (wire) | An exotic alloy sometimes used in making springs. |
| Pigtail | A form taken by tie wire when used to secure a bundle of heavy spring wire. |
| Pitch | The distance, center to center, between two active coils of a compression spring. |
| Spring [dia] | A helically formed piece of (usually) wire which derives its usefulness because it tries to regain its original shape when subjected to a load. See Compression Spring, Extension Spring, Torsion Spring. |
| Stainless Steel (wire) | An alloy used in making springs that will not rust. The most common stainless steels are called 302 and 17-7. |
| Stress | Misalignment of the molecules in wire due to bending. |
| Titanium | A strong, lightweight metal sometimes used in making springs. |
| Tool post | The part of a lathe that allows tooling to be mounted and used on stock. |
| Torsion | Twisting. |
| Torsion spring | A spring which derives its usefulness by trying to return to its original shape when subjected to a load traveling around its axis. |
| Variable pitch | A form of compression spring that has more than one pitch. |
| Wind | To coil (a spring). |
| Wire | Metal, usually round and solid in section, used in making springs. |